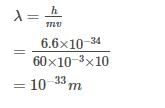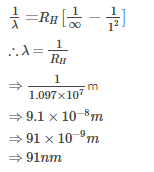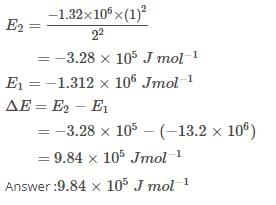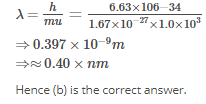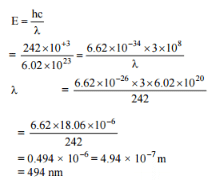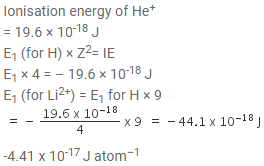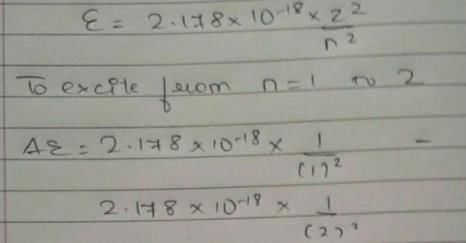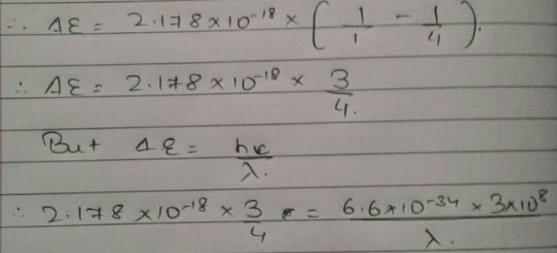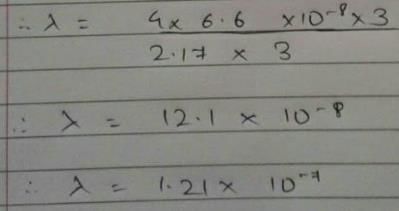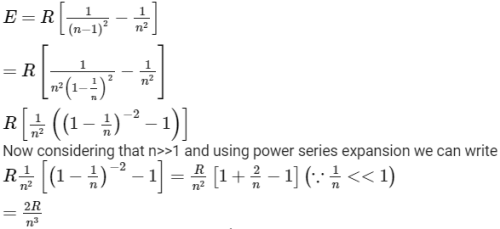Test: JEE Previous Year Questions- Structure of Atom - JEE MCQ
28 Questions MCQ Test - Test: JEE Previous Year Questions- Structure of Atom
An atom has a mass of 0.02 kg & uncertainity in its velocity is 9.218 × 10-6 m/s then uncertainity in position is (h = 6.626 × 10-34 J - s) [AIEEE- 2002]
Energy of H–atom in the ground state is -13.6 eV , Hence energy in the second excited state is–
Uncertainty in position of a particle of 25 g in space is 10-5 m. Hence uncertainty in velocity (ms-1) is (Planck's constant h = 6.6 × 10-34 Js) [AIEEE- 2002]
The orbital angular momentum for an electron revolving in an orbit is given by . This momentus for an s-electron will be given by - [AIEEE- 2003]
In Bohr series of lines of hydrogen spectrum, third line from the red end corresponds to where one of the following inter-orbit jumps of electron for Bohr orbits in an atom of hydrogen. [AIEEE- 2003]
The de Broglie wavelength of a tennis ball mass 60 g moving with a velocity of 10 mt. per second is approximately - [AIEEE- 2003]
Which of the following sets of quantum numbers is correct for an electron in 4f orbital ? [AIEEE- 2004]
Consider the ground state of Cr atom (Z = 24). The numbers of electrons with the azimuthal quantum numbers, l = 1 and 2 are, respectively [AIEEE- 2004]
The wavelength of the radiation emitted, when in a hydrogen atom electron falls from infinity to stationary state 1, would be (Rydberg constant = 1.097×107 m-1) [AIEEE- 2004]
Which one of the following sets of ions represents the collection of isoelectronic species ? [AIEEE- 2004]
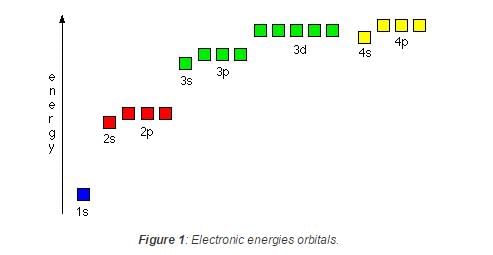
In a multi-electron atom, which of the following orbitals described by the three quantum members will have the same energy in the absence of magnetic and electric fields ? [AIEEE- 2005]
(a) n = 1, l = 0, m = 0
(b) n = 2, l = 0, m = 0
(c) n = 2, l = 1, m = 1
(d) n = 3, l = 2, m = 1
(e) n = 3, l = 2, m = 0
Of the following sets which one does NOT contain isoelectronic species ? [AIEEE- 2005]
According to Bohr's theory, the angular momentum of an electron in 5th orbit is - [AIEEE 2006]
Uncertainty in the position of an electron (mass = 9.1 × 10-31 kg) moving with a velocity 300 m/s, accurate upto 0.001 %, will be (h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js) [AIEEE 2006]
Which of the following sets of quantum numbers represents the highest energy of an atom ? [AIEEE 2007]
The ionization enthalpy of hydrogen atom is 1.312 × 106 J mol-1. The energy required to excite the electron in the atom from n = 1 to n = 2 is [AIEEE 2008]
In an atom, an electron is moving with a speed of 600 m/s with an accuracy of 0.005%. Certainity with which the position of the electron can be located is (h = 6.6×10-34 kg m2s-1 ,mass of electron, em = 9.1×10-31 kg ) [AIEEE 2009]
Calculate the wavelength (in nanometer) associated with a proton moving at 1.0×103ms-1
(Mass of proton = 1.67×10-27 kg and h = 6.63×10-34 Js ) : [AIEEE 2009]
The energy required to break one mole of Cl - Cl bonds in Cl2 is 242 kJ mol-1. The longest wavelength of light capable of breaking a single Cl - Cl bond is(c = 3 x 108 ms-1 and NA = 6.02 x 1023 mol-1) [AIEEE 2010]
Ionisation energy of He+ is 19.6 x 10-18 J atom-1. The energy of the first stationary state (n = 1) of Li2+ is
[AIEEE 2010]
Iron exhibits +2 and +3 oxidation states. Which of the following statements about iron is incorrect ?
[AIEEE 2012]
The electrons identified by quantum numbers 'n' and l : [AIEEE 2012]
(a) n = 4, l = 1
(b) n = 4, l = 0
(c) n = 3, l = 2
(d) n = 3, l = 1
can be placed in order of increasing energy as :
The standard reduction potentials for Zn2+/Zn, Ni2+/Ni, and Fe2+/Fe are -0.76, -0.23 and -0.44 V respectively. The reaction X + Y2+ → X2+ + Y will be spontaneous when: [AIEEE 2012]
The first ionisation potential of Na is 5.1 eV. The value of electron gain enthalpy of Na+ will be:
[AIEEE 2013]
Energy of an electron is given by E = -2.178 × 10-18 Wavelength of light required to excite an electron in an hydrogen atom from level n = 1 to n = 2 will be (h = 6.62 × 10-34 Js and c = 3.0 × 108 ms-1)
[AIEEE 2013]
Which of the following is the wrong statement ? [AIEEE 2013]
Which of the following arrangements does not represent the correct order of the property stated against it?
[AIEEE 2013]
In a hydrogen like atom electron make transition from an energy level with quantum number n to another with quantum number (n - 1). If n >> 1, the frequency of radiation emitted it proportional to [AIEEE 2013]